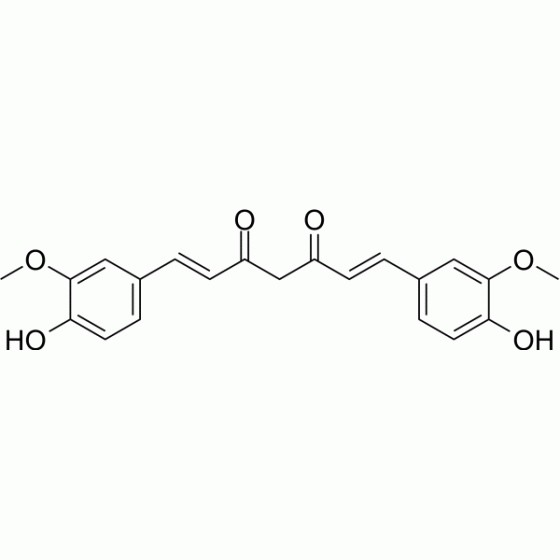
Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane),是一种天然酚类化合物,是乙酰转移酶 p300/CREB 结合蛋白 特异性抑制剂,抑制组蛋白/非组蛋白的乙酰化和组蛋白乙酰转移酶依赖的染色质转录。Curcumin 对 NF-κb 和 MAPKs 有抑制作用,并具有抗炎、抗氧化、抗增殖和抗血管生成等多种药理作用。Curcumin 通过 Keap1 半胱氨酸修饰诱导 Nrf2 蛋白的稳定。
| 生物活性 |
Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane), a natural phenolic compound, is a p300/CREB-binding protein-specific inhibitor of acetyltransferase, represses the acetylation of histone/nonhistone proteins and histone acetyltransferase-dependent chromatin transcription. Curcumin shows inhibitory effects on NF-κB and MAPKs, and has diverse pharmacologic effects including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiproliferative and antiangiogenic activities. Curcumin induces stabilization of Nrf2 protein through Keap1 cysteine modification. |
||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 & Target |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Curcumin exerts its chemopreventive effects partly through the activation of nuclear factor (erythroid-2 related) factor 2 (Nrf2) and its antioxidant and phase II detoxifying enzymes[1]. Curcumin inhibits T47D cells growth, with IC50s of 25, 19 and 17.5 μM for 24, 48 and 72 h MTT assays respectively. IC50s of curcumin and silibinin mixture against T47D cells, are 17.5, 15, and 12 μM for 24, 48, and 72 h exposure times, respectively[2]. Curcumin (2.5-80 μM) induces apoptotic cell death in AGS and HT-29 cell lines, and the IC50 is 21.9±0.1, 40.7±0.5 μM, respectively, in both AGS and HT-29 cell lines. Curcumin-induced apoptosis requires caspase activities in AGS and HT-29 cells. Curcumin induces ER Ca2+ decline and mitochondrial Ca2+ overloading[3]. Curcumin induces the G2/M cell cycle arrest of LNCaP and PC-3 cells in a dose dependent manner. Curcumin upregulates the protein level of NF-kappaB inhibitor IkappaBalpha and downregulates protein levels of c-Jun and AR[5]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Curcumin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly prevents decrease in the percentage of sucrose consumption, as compared to the CMS-exposed rats. Curcumin treatment results in significant prevention of increase in TNF-α and IL-6 levels in stressed rats[4]. Curcumin decreases binding of p300/CREB-binding protein (CBP) at the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promoter at 20 mg/kg (i.p.), reduces binding of P300/CBP at the BDNF promoter at 40 mg/kg, and decreases binding all the four proteins of p300/CBP and H3K9ac/H4K5ac at the BDNF promoter at 60 mg/kg in chronic constriction injury (CCI) rats[6]. MCE has not independently confirmed the accuracy of these methods. They are for reference only. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Clinical Trial |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 分子量 |
368.38 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 性状 |
固体 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Formula |
C21H20O6 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS 号 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 中文名称 |
姜黄素;酸性黄;姜黄色素 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 结构分类 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 初始来源 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature in continental US; may vary elsewhere. |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 储存方式 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| 溶解性数据 |
In Vitro:
DMSO 中的溶解度 : 100 mg/mL (271.46 mM; 超声助溶; 吸湿的 DMSO 对产品的溶解度有显著影响,请使用新开封的 DMSO) 配制储备液
查看完整储备液配制表
* 请根据产品在不同溶剂中的溶解度选择合适的溶剂配制储备液;一旦配成溶液,请分装保存,避免反复冻融造成的产品失效。 |
| 其它 | |
| weight | 1mg |